Raster vs Vector Images: The Key Differences Explained

estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Raster vs Vector: Understanding These Two Popular Image Formats
When it comes to digital graphics, there are two primary
types of images: Raster and Vector.
Each has unique strengths and limitations, so it is
important to understand how these two image formats differ. Selecting the right
one for your specific project can mean the difference between a crisp,
professional-looking image and one that appears blurry or distorted.

In this article, we'll explain what Raster and Vector images
are, how they differ, and the best uses for each.
What Are Raster Images?
Raster Images, sometimes referred to as Bitmaps, are made up
of thousands upon thousands of tiny individual squares called pixels.
Each pixel displays a specific color value. Arranged in a grid-like
formation, pixels are the fundamental building blocks of a Raster image.
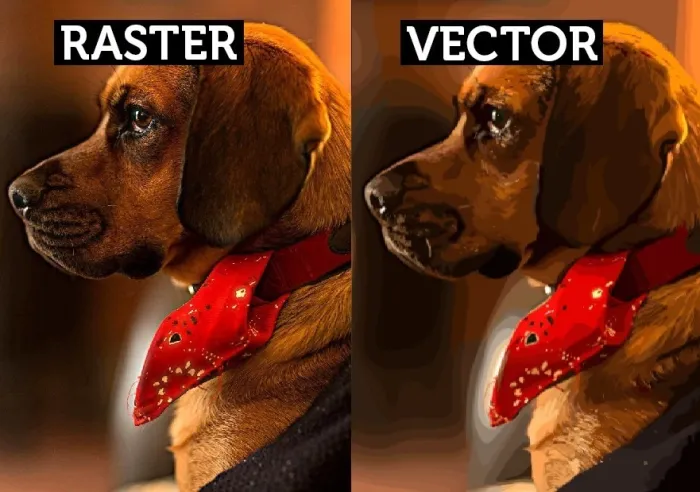
When viewed collectively at normal size, the pixels form a
complete image with smooth color transitions. However, if you were to increase
the dimensions of a Raster image beyond its original size, the individual square-shaped
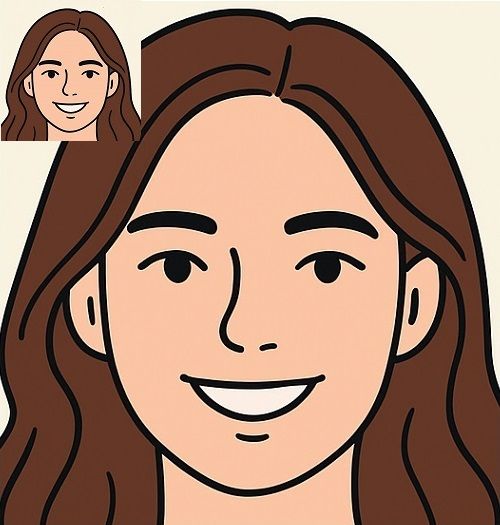
pixels become more visible, distorting the image (see example image below).
What are the most common Raster File Formats?
- JPEG (.jpg) - Joint Photographic Experts Group
- PNG (.png) - Portable Network Graphics
- TIFF (.tif) - Tagged Image File Format
- GIF (.gif) - Graphics Interchange Format
- BMP (.bmp) - Bitmap

What are the Advantages of Raster Images?
Intricate Detail and Realism - a Raster image can display
fine details, complex color variations, and subtle gradients. This makes it the
ideal file format for photographs and realistic artwork.
Universally Compatible - common Raster file formats (.jpg,
.png, .tif, .gif, .bmp) have widespread compatibility with most operating
systems, design software, and devices.
Precision Image Retouching - because Raster images are pixel-based,
this allows for precise image adjustments at the individual pixel level. For
examples, pixels can be added or removed, or have various attributes altered such
as color and brightness.
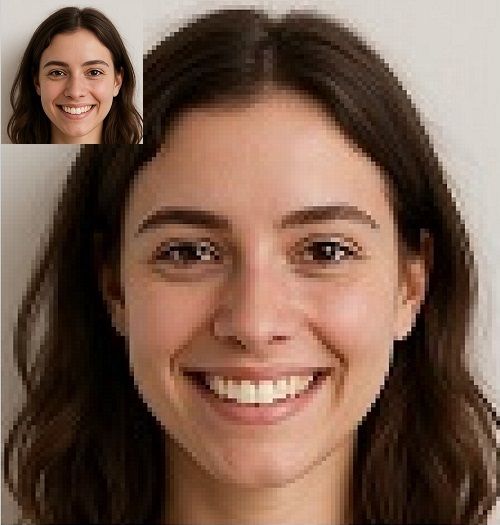
What are the Limitations of Raster Images?
Quality Decreases when Enlarged - a Raster image is resolution-dependent,
so enlarging a Raster beyond its original size merely stretches the existing pixels. This results in less detail, not more. Also, as the pixels gain size, their square
edges become more visible. This leads to a jagged appearance and reduces the
sharpness of the image.
Larger File Sizes - high-resolution Raster images require a
lot of storage space, especially as the dimensions and pixel counts increase.
Unsuitable for Certain Graphics - because Raster files are
composed of a fixed grid of pixels, they lack the flexibility needed for logos,
icons, and illustrations that require sharp lines and infinite scalability.

What Are Vector Images?
Vector Images are created in a completely different way from Raster images. Instead of being pixel-based, Vector images use mathematical formulas to define shapes - using points, lines, and curves - into which various fill colors are placed.
In other words, a Vector file does not store a finite
grid of colored pixels, it stores instructions for how the image should be
drawn.
Because Vector images are defined by mathematical formulas instead of a fixed grid, they can be scaled infinitely - up or down - without losing image quality. The formulas for the shapes and color fills are simply recalculated at the new size.
This means the same Vector logo will look crisp
and sharp whether printed on a small item, like a business card or envelope, or
on a large item like a banner or tradeshow backdrop.
What are the most common Vector File formats?
- AI (.ai) - Adobe Illustrator
- EPS (.eps) - Encapsulated PostScript
- SVG (.svg) - Scalable Vector Graphics
What are the Advantages of Vector Images?
Infinite Scalability - because Vector graphics are based on mathematical formulas, they are resolution-independent. As such, they can be easily resized up or down without losing clarity.
Smaller File Sizes - compared to high-resolution Raster images, Vector files are usually much smaller in size. This is because they only store instructions for generating shapes and colors rather than data for thousands or millions of pixels.
Easier to Edit Individual Elements - the design components
within a Vector image, such as shapes, lines, text, and colors can be adjusted
independently without affecting the entire image. Hence, Vectors are very
flexible for design changes.
What are the Limitations of Vector Images?
Not Suited for Complex Images - Vector graphics are limited
in their ability to represent detailed photographs or images with continuous color
gradients, shadows, or textures.
Limited Realism - Vectors are excellent for creating clean,
flat designs, but they aren't able to replicate the natural look of real-world
objects the way Raster images can.
Potential for Software Incompatibility - some programs or platforms may
not fully support Vector file formats, potentially requiring conversion that
could lead to a loss of quality or features.
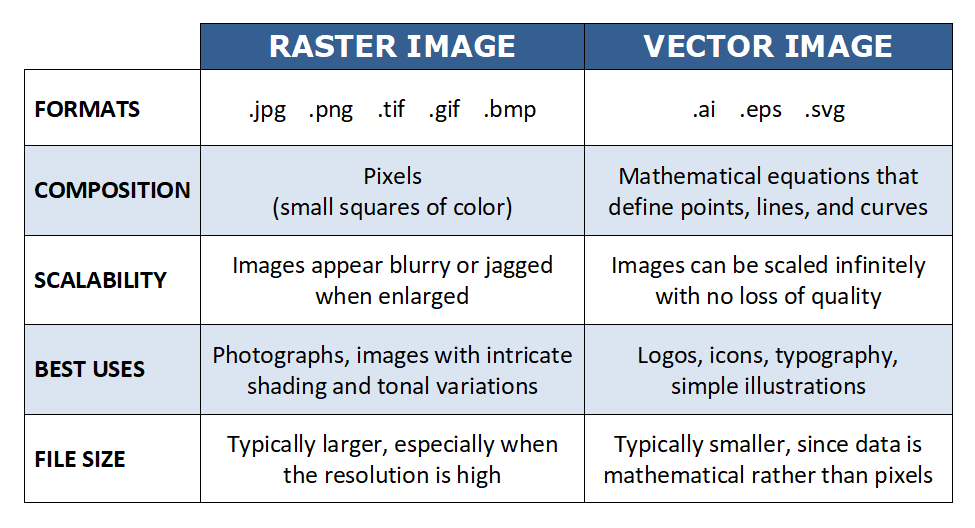
Raster vs Vector: Key Differences at a Glance...
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between Raster and Vector
graphics is essential for anyone working with digital images. Here's a quick
review…
Raster Images are the perfect choice for photographs or complex
visuals. If a project involves detailed shading, textures, or a wide range of
colors, Raster is the better option.
Vector Images are the perfect choice for logos, icons,
typography, and illustrations. If a project requires clean design and unlimited
scalability, Vector is the better option.
Color Vision is always ready to help!
If you have any print-related questions or have an upcoming
print project, be sure to get in touch with Color Vision Printing. Our friendly
and experienced staff is always ready to serve you. Plus, you'll be pleased
with our affordable pricing on digital printing, offset printing, finishing,
and binding.
To get a price quote, use our simple Quote Request form to
send us your project's specifications and we will be happy to email a custom
quote to you. Or, if you prefer to discuss your project by phone, give us a
call at 800-543-6299.
As always, we hope to hear from you soon and look forward to assisting with your printing needs!
Related Articles

Commercial Printing: What does “Halftone” mean?
Read This Article
The Difference between CMYK and RGB Color Models
Read This Article

White Space: The Importance of White Space in Graphic Design
Read This Article

Printing Terminology: What are Crop Marks?
Read This Article